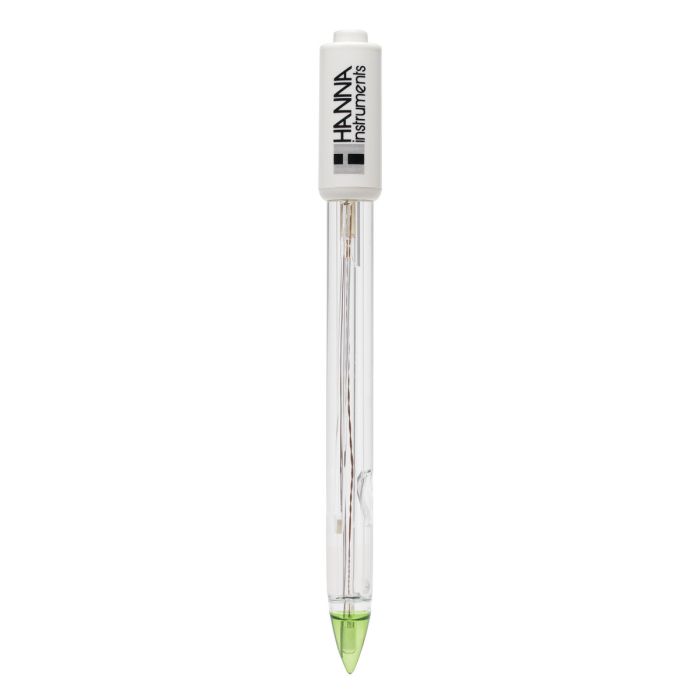
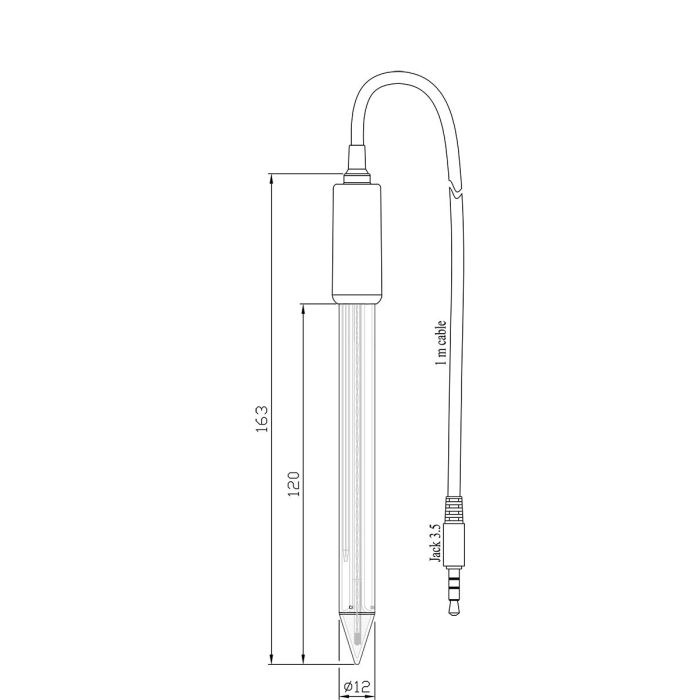
Built-In Microchip
The built-in microchip stores sensor type, serial number and calibration information including date, time, offset, slope, probe condition and buffers used. This information is automatically retrieved by edge® once the electrode is plugged in. The ability to transfer information allows for hot swapping of probes without having to recalibrate. All pH measurements are performed within the electrode and transferred digitally to the meter. This overcomes any noise issues associated with the traditional high impedance analog measuring system. Electrical noise can be generated from a built in temperature sensor and while working in a humid environment.
Conical Glass Tip
The conical shaped tip design allows for penetration into solids, semi solids, and emulsions for the direct measurement of pH in food products including meat, cheese, yogurt, and milk. The glass tip uses a special LT (low temperature) glass formulation with a lower resistance of approximately 50 megaohms compared to GP (general purpose) glass with a resistance of about 100 megaohms. This is beneficial since many food products are stored at low temperatures. As the temperature of the glass decreases in the sample, the resistance of the LT glass will approach that of GP glass. If using GP glass, the resistance would increase above the optimum range, resulting in increased impedance and ultimately affecting the measurement.
Open Reference Junction
Suspended solids and proteins found in food products will clog a conventional ceramic reference junction. This clogging will impede the measurement circuit between the indicating glass electrode and the internal reference resulting in slower response time, erratic readings and frequent electrode replacement. The open junction design consists of a solid gel (viscolene) interface between the sample and internal Ag/AgCl reference. This interface not only prevents silver from entering the sample, but also makes it impermeable to clogging, resulting in a fast response and stable readings.
Glass Electrode Body
The glass electrode body is suitable for a wide range of applications due to its chemical resistance. The glass electrode is compatible with many non-aqueous solvents and other aggressive chemicals. Glass is also resistant to many forms of radiation, such as ultraviolet radiation.
Purchase & Shipping
All prices are inclusive of GST and not all items are stock items, if you require an immediate solution, please send an email to sales@hannainst.com.au or call us on (03) 9769 0666.
Free standard delivery: Free shipping applies to online orders over $150 placed via our website within Australia, typically arriving within 5 to 7 days. Delivery times may vary depending on the courier service and the recipient’s location. Free shipping is not available with other offers or discounts.
Same-day dispatch: Place your order before 1 PM Monday to Friday for same-day despatch (leaves our warehouse). Delivery times may vary depending on the courier service and the recipient’s location. Subject to stock availability.
Please note that we do not offer shipping to PO Box addresses.