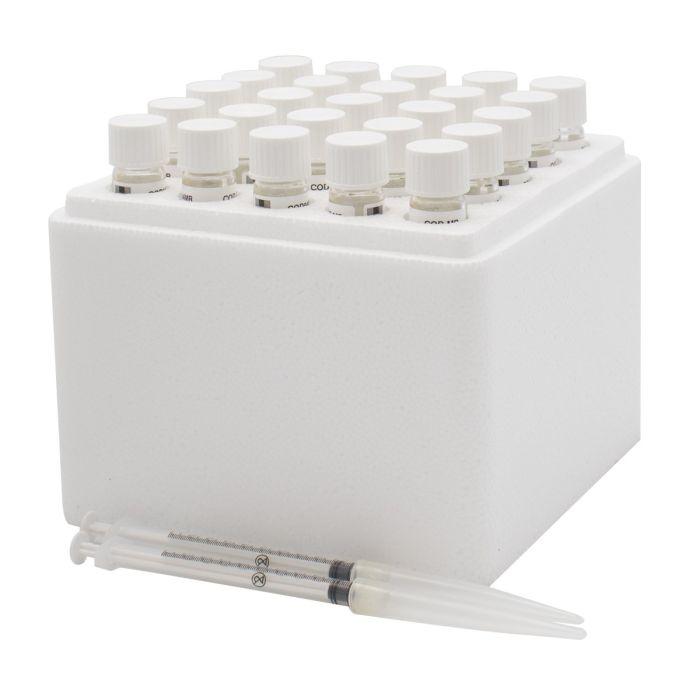
The HI94754F-25 COD kit contains 25 ready-to-use, barcoded vials containing pre-measured reagents. These high quality reagents follow the ISO approved method 15705. In this method, a heated digestion is required to oxidize organic matter in the sample. During the digestion, hexavalent chromium in the reagent is reduced to trivalent chromium. The amount of reduced chromium is then measured colorimetrically. The intensity of color is determined by a compatible photometer and the COD concentration is displayed in mg/L (ppm) O2. These reagents are designed to be used with samples that have an expected range of 0 to 150 mg/L (ppm) O2. Automatic recognition of barcoded samples is an exciting feature when using the HI94754F-25 reagent vials with a barcode compatible photometer. When inserted into the vial holder of the photometer, the sample method and range are automatically identified from the barcode. The barcode has four digits: the first two digits are for parameter identification and the second two digits are for reagent lot ID. Vials for different COD methods can be distinguished by a barcode printed on the vial – the barcodes for different methods are shown in the table below.
Comparison of Methods
EPA – The EPA approved method 410.4 for COD determination requires the use of mercuric sulfate (HgSO4). Mercuric sulfate is present in the EPA reagent vials to mitigate the interference of chloride in the measurement sample. This is a common requirement for wastewater treatment plants and food manufacturing facilities which tend to have higher concentrations of chloride present in their effluent. When using reagents that follow the EPA method, it is important to treat used vials as hazardous waste, as mercury waste requires recycling.
Dichromate – The dichromate method is adapted from the standard EPA and ISO methods for determination of COD, which are approved to measure COD concentrations ranging up to 1500 mg/L O2. For samples with expected concentrations in the high range of 0 to 15000 mg/L O2, the dichromate reagents can be used for accurate COD determination. It is important to treat used vials as hazardous waste, as mercury waste requires recycling.
Mercury-free – For those who do not wish to handle mercury reagents, our “green, ” mercury-free reagents are available for COD determination. These reagents are more sensitive to chloride interferences, as mercuric sulfate is not present. While the mercury-free reagents are easier to dispose of, they may be unacceptable for reporting purposes.
ISO – The ISO approved method 15705 for COD determination also requires the use of mercuric sulfate (HgSO4) to reduce the interference of chloride. Containing similar chemical reagents as the EPA method, it is important to treat used ISO vials as hazardous waste, as mercury waste requires recycling.
|
Method
|
Parameter |
Range (as O2) |
Resolution |
Accuracy |
Reagent Code |
|
EPA
|
COD LR
|
0 to 150 mg/L |
1 mg/L |
±5 mg/L ±5% of reading |
HI94754A-25 |
| COD MR |
0 to 1500 mg/L |
1 mg/L |
±15 mg/L ±4% of reading |
HI94754B-25
|
|
Dichromate
|
COD HR |
0 to 15000 mg/L |
10 mg/L |
±150 mg/L ±3% of reading |
HI94754C-25
|
|
Mercury-free
|
COD LR |
0 to 150 mg/L |
1 mg/L |
±5 mg/L ±5% of reading |
HI94754D-25 |
|
COD MR
|
0 to 1500 mg/L |
1 mg/L |
±15 mg/L ±4% of reading |
HI94754E-25
|
|
ISO
|
COD LR |
0 to 150 mg/L |
1 mg/L |
±5 mg/L ±5% of reading |
HI94754F-25 |
| COD MR |
0 to 1500 mg/L |
1 mg/L |
±15 mg/L ±4% of reading |
HI94754G-25
|
Purchase & Shipping
All prices are inclusive of GST and not all items are stock items, if you require an immediate solution please send an email to sales@hannainst.com.au or call us on (03) 9769 0666.
Free standard delivery: We offer free delivery within Australia on orders over $150, typically arriving within 5 to 7 days. Delivery times may vary depending on the courier service and the recipient's location. Free shipping is not available with other offers or discounts.
Same-day dispatch: Place your order before 1 PM Monday to Friday for same-day despatch (leaves our warehouse). Delivery times may vary depending on the courier service and the recipient's location. Subject to stock availability.
Please note that we do not offer shipping to PO Box addresses.