Hanna Instruments offers a diverse range of pH electrodes tailored to suit various applications. Key design features include the type of sensing glass, bulb shape, body material, junction style, reference system, and electrolyte.
The HI1143B electrode features a fluoride-resistant (HF) glass formulation, spherical tip, glass body, single ceramic frit, double junction design, and is refillable with 3.5M KCl solution.
Fluoride-Resistant Glass
Fluoride ions can degrade standard glass bulbs, significantly shortening electrode lifespan. The HI1143B uses HF-resistant glass, making it suitable for demanding applications involving fluoride for improved durability.
Spherical Bulb
Designed for general-purpose use, the spherical bulb ensures reliable measurements in a variety of sample types. For specialized needs, other tip shapes—like conic for piercing or flat for surface measurements—are available across our range.
Glass Body
Ideal for laboratory environments, the glass body resists aggressive chemicals and is easy to clean. It also facilitates rapid heat transfer to the internal electrolyte, helping the electrode reach thermal equilibrium quickly for more stable readings.
Single Ceramic, Double Junction Reference
This electrode uses a double junction system with a single ceramic frit in the outer reference. The porous ceramic allows a steady ion exchange at a flow rate of 15–20 µL/hour. The double junction helps prevent contamination from the sample into the reference, which is particularly beneficial in complex or reactive solutions.
Refillable Design
The HI1143B is refillable with HI7082 3.5M KCl electrolyte, free of silver. This prevents silver-based precipitates from forming and potentially clogging the junction, which can lead to unstable or erratic readings.
BNC Connector
Equipped with a universal BNC connector, the HI1143B is compatible with any meter accepting this standard input. Other connector types such as DIN, screw, T-type, and 3.5mm are more meter-specific and not interchangeable.
Single Junction Versus Double Junction pH Electrodes
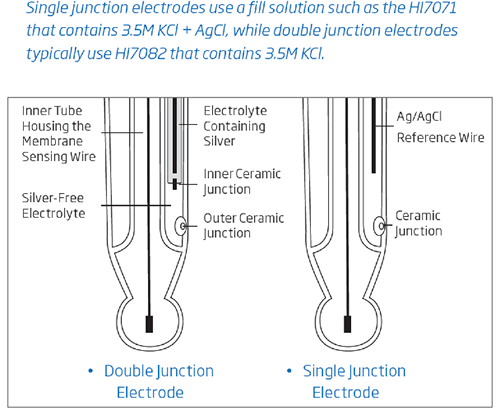
Traditional electrodes typically feature a single junction design. As illustrated above, this configuration includes one junction connecting the internal reference wire to the external solution. In challenging environments—such as those involving high pressure, extreme temperatures, or strongly acidic or alkaline media—the normal outward flow of electrolyte may reverse. This reversal allows the sample to enter the reference compartment, which can contaminate the reference system and eventually lead to electrode failure.
Another common issue with single junction electrodes is junction clogging due to silver chloride (AgCl) precipitation. In the presence of Tris buffer or heavy metals, silver ions can react and form AgCl deposits when the electrolyte contacts the sample. These deposits build up on the outer junction surface, often resulting in unstable and drifting readings.
Hanna’s double junction electrodes address these limitations by incorporating two junctions, with only the outer one exposed to the sample. In harsh conditions, while sample ingress may still occur, the reference system remains better protected because it is isolated from direct contact. Additionally, the outer compartment is filled with a silver-free electrolyte. This prevents the formation of silver chloride precipitate, significantly lowering the risk of junction clogging and improving overall electrode reliability and longevity.
Purchase & Shipping
All prices are inclusive of GST and not all items are stock items, if you require an immediate solution please send an email to sales@hannainst.com.au or call us on (03) 9769 0666.
Free standard delivery: We offer free delivery within Australia on orders over $150, typically arriving within 5 to 7 days. Delivery times may vary depending on the courier service and the recipient’s location. Free shipping is not available with other offers or discounts.
Same-day dispatch: Place your order before 1 PM Monday to Friday for same-day despatch (leaves our warehouse). Delivery times may vary depending on the courier service and the recipient’s location. Subject to stock availability.
Please note that we do not offer shipping to PO Box addresses.






