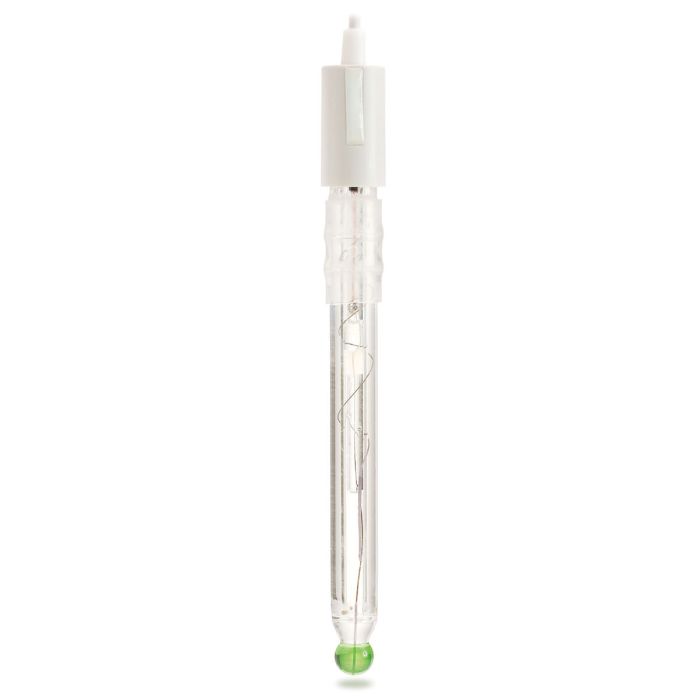
The FC300B sodium ion selective electrode is a combination electrode that has a silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) reference and a sodium ion selective electrode. Both are housed within a single glass body design that uses an ammonium chloride/silver chloride electrolyte for a fill solution.
The sodium sensitive membrane should be conditioned before performing a calibration. The conditioning of the electrode is a two-step process in which the glass is etched then rehydrated. The first step is etching. This process removes a thin layer of sensitive glass from the sodium membrane, exposing a sodium-containing fresh surface. The second step is rehydration in which the probe is placed in storage solution to rehydrate the glass membrane. Allowing the glass to rehydrate after etching provides optimum conditions for the exchange of sodium ions between the membrane and solution.
For the FC300B to measure sodium accurately, it is important that the ionic strength of the standards and sample be adjusted to a high and constant value with the sodium ionic strength adjuster (ISA) solution. The sodium ISA is important for two reasons. One is that the ISA buffers the pH of the standard and sample to above pH 9.8. This removes any interference from hydrogen ions that occur at lower pH’s. The second purpose of the ISA is to ensure that the activity coefficient is constant so the concentration of free sodium ions can be measured. Having solutions with a constant ionic strength reduces the margin of error between measurements of different samples at different concentrations.
The FC300B sodium glass ISE can measure from 10µM (0.23 mg/L) to 1M (22, 990 mg/L).
Conversion Table for Na+ and NaCl
|
Multiply |
| moles/L (M) Na+ to ppm (mg/L) Na+ |
22990 |
| ppm (mg/L) Na+ to M (moles/L) Na+ |
4.35 x 10-5 |
| ppm (mg/L) Na+ to ppm (mg/L) NaCl |
2.54197 |
| ppm (mg/L) NaCl to ppm (mg/L) Na+ |
0.39339 |
Features at-a-glance
Spherical Glass Tip – The spherical shaped tip design allows for a wide area of contact with the sample, permitting a faster electrode response with a higher degree of stability.
Glass Electrode Body – The glass electrode body is suitable for a wide range of applications due to its chemical resistance. The glass electrode is compatible with many non-aqueous solvents and other aggressive chemicals. Glass is also resistant to many forms of radiation, such as ultraviolet radiation.
BNC Connection -The FC300B has a universal BNC connector for easy connection to any benchtop meter with a female BNC probe input.
Theory of Operation
A glass ion selective electrode develops a voltage due to the ion exchange that occurs between the solution and the sensing membrane. The selective glass membrane blown on the tip of the sensor exchanges ions with the solution being measured. The charge imbalance between the membrane surface and internal cell of the sensor produces a voltage that changes in response to the sample’s ion activity. When the ionic strength of the solution is fixed by the addition of ISA, the voltage is proportional to the concentration of free ions in solution.
Purchase & Shipping
All prices are inclusive of GST and not all items are stock items, if you require an immediate solution please send an email to sales@hannainst.com.au or call us on (03) 9769 0666.
Free standard delivery: We offer free delivery within Australia on orders over $150, typically arriving within 5 to 7 days. Delivery times may vary depending on the courier service and the recipient's location. Free shipping is not available with other offers or discounts.
Same-day despatch: Place your order before 1 PM Monday to Friday for same-day despatch (leaves our warehouse). Delivery times may vary depending on the courier service and the recipient's location. Subject to stock availability.
Please note that we do not offer shipping to PO Box addresses.